development theory
- Metabolism.Changes in intervertebral disc metabolism due to dehydration (water content is 88% in youth, reducing to 60% with age).
- Blood vessel.Changes in spinal cord circulation (occurs in adulthood but may also occur in early development due to injury, metabolic disorders, infection).
These theories are sometimes combined into one - the involution theory, which is based on the violation of nutrition, especially in those tissues without blood vessels. During childhood, there is a network of blood vessels within the disc, but after the spinal structure is fully formed, this network is closed by connective tissue. - hormonal theoryMore controversial. Hormone status plays a certain role in the occurrence and development of osteochondrosis, but it is inappropriate to refer only to hormone levels. This theory is most relevant to postmenopausal women.
- Mechanical theoryTalk about the connection between the development of osteochondrosis and overloading certain parts of the spine.
- anomaly theory- An isolated case in mechanical theory. Vertebral abnormalities, vertebral body fusion, and vertebral arch nonfusion due to improper biological mechanisms can stimulate overloading of the intervertebral discs and lead to bone tissue destruction.
Factors that lead to disease development
- Gravity coefficient:For the spine, any non-physiological displacement does nothing more than trigger many muscle reactions.
- Dynamic factors:The greater the load on the spine and the longer it lasts, the more trauma it takes and the longer it lasts (people who are easily forced to hold positions for long periods of time; constantly lifting heavy objects).
- Metabolic disorders factors:Undernutrition of the spine due to autoimmune disease, toxic effects.
It is known that eating food from aluminum cutlery can cause it to accumulate in the bones, leading to the development of osteochondrosis. Eating food in aluminum-iron alloy tableware has adverse effects on the human body. When preparing food, particles enter the gastrointestinal tract, and since they also contain lead, this metal can accumulate in the body, with poisoning manifesting itself as neuroosseofibrosis (defects in the tissue at the junction of tendons and muscles). - genetic factors.Everyone has their own level of flexibility, which is directly related to the ratio of fibers in the connective tissue (collagen and elastin) and is hereditary. Still, the proportions of fibers are regulated; deviations can cause the spine to wear out more quickly.
- biomechanical factors– Non-physiological movements of the articular surfaces of the spine. This is caused by muscle atrophy (clinical sign is pain when bending and turning).
- sterile inflammatory factors– The most common is a rapid inflammatory process in the intervertebral discs. Microscopic defects develop in the spine due to disc dystrophy. Within these microdefects, areas of dead tissue form.
Symptoms of spinal osteochondrosis
Osteochondrosis is a common disease among athletes. It is caused by the difference between physiological capacity and exercise load, which results in microtrauma and wear and tear on spinal tissues.
| Types of osteochondrosis | cervix | Chest | lumbosacral region | mix |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| clinical picture |
|
|
|
|
| complication |
|
|
stages of osteochondrosis
| stage | first | second | third | fourth |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| changes in spine |
|
|
The disc ruptures and displaces, and other surrounding elements immerse into its cavity, causing the development of local inflammatory symptoms. | Destruction of other elements of the intervertebral joint, pathological arrangement of the joint surfaces, marginal bone growth. |
| patient complaints | No or showing discomfort when remaining in the same position for extended periods of time. | Certain types of exercise can cause discomfort and pain. | Pain in the back, neck, lower back, sacrum, or tailbone, depending on the location. | Persistent pain throughout the spine. |
Differential diagnosis
- Acute myocardial infarction.The pain is concentrated in the heart area and only radiates (spreads) from there to the neck, jaw, and arms. The disease begins for no apparent reason or occurs after physical activity with compressive pain that is not related to spinal movement. Half an hour later, the pain reached its worst, and the patient developed shortness of breath and fear of death. Diagnosis is confirmed by electrocardiogram (ECG) and markers of myocardial necrosis.
- subarachnoid hemorrhage(bleeding between the arachnoid and pia mater of the brain). In some cases, severe pain in the spine may occur due to the toxic effects of the spilled blood on the base of the spine. The main clinical symptom is the presence of blood in the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Spinal abnormalities.Minimum examination: Frontal and side projection X-rays of the skull and cervical spine. The most common abnormalities of the spine are: fusion of the atlas (first cervical vertebra) with the occipital bone, depression of the edge of the occipital foramen into the cranial cavity, fusion of vertebrae, and changes in the shape and size of the vertebrae. vertebra.
- cervical lymphadenitisThere may also be neck pain, sometimes worsened by bending and turning. The diagnosis was not difficult: swollen, painful lymph nodes; a history of frequent sore throats.
- Multiple myeloma.Pain in the spine develops gradually against the background of gradual weight loss and periodic fevers. The main laboratory indicator is protein in urine.
- Spinal tumors or metastases.Evidence supporting malignancy is: progressive weight loss, laboratory changes, and ultrasonography of the source of metastasis (kidney, lung, stomach, thyroid, prostate).
- Rheumatic and infectious allergic polyarthritisDifferentiation is based on medical history, moderate elevation of body temperature, and major damage to large joints.
- Depression in disguise.Patients "imposed" non-existent pathology (in this case, symptoms of osteochondrosis), tried to explain to them the essence of what was happening, but encountered misunderstandings. Symptoms of covert depression include: decreased mood, concentration, and performance; sleep and appetite disturbances; and suicidal thoughts and behaviors.
- Peptic ulcers of the stomach and duodenum, pancreatitis and cholecystitisDiagnosis is made by association of pain with food intake, laboratory tests (FGDS, general blood tests, biochemical blood tests, pancreatic enzyme activity, ultrasonography of abdominal organs).
Diagnosis of osteochondrosis
- Most commonly, patients complain to a neurologist, who takes a history of the patient's life and condition and performs a neurological examination. Neurologists examine the spine in three ways (standing, sitting, and lying down). When examining the back, pay special attention to posture, the inferior angle of the shoulder blades, the iliac crest, the position of the shoulder girdle, and the expression of the back muscles. During palpation, deformity, pain, and muscle tone can be determined.
- When confirming the diagnosis of osteochondrosis, additional consultation with specialized experts is required to exclude conditions with similar symptoms (cardiologists, therapists, rheumatologists).
- Perform mandatory laboratory tests (general blood test, general urinalysis, blood chemistry test).
- Proven research can help:
- Radiography of two projections of the spine– The easiest way to identify changes in the spine (narrowing of the spaces between vertebrae);
Depending on the degree, various changes can be seen on radiographs: degree first second third fourth X-ray signs There are no radiological signs. Changes in disc height. The disc may herniate (bulge into the spinal canal) or even herniate (fall off). Osteophytes (marginal bone growth) form at the contact points of the vertebrae. - Computed tomography (CT) and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)– Not only for identifying changes in the spine, but also for determining pathological conditions in other organs;
- USDG MAG (Ultrasound Doppler of Cephalic Aorta)– Ultrasound examination of the circulatory system of the head and neck allows you to diagnose the degree of vascular changes as early as possible.
- Radiography of two projections of the spine– The easiest way to identify changes in the spine (narrowing of the spaces between vertebrae);
What are the treatments for osteochondrosis?
- Pain relief is provided with the help of analgesics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). NSAID treatment should be given for as short a time as possible; 5-7 days is sufficient for pain relief. If pain control is poor and you need to continue taking painkillers, you can take a selective COX-2 inhibitor.
- Antispasmodics reduce pain and relieve muscle spasms.
- Transcutaneous analgesic methods: ointment, the active ingredient of which is NSAID; anesthetic ointment; combined with anti-inflammatory and analgesic drugs, and the addition of corticosteroids has a better effect.
- Treatments aimed at regenerating inflamed or compressed nerves and improving blood microcirculation: B vitamins, neuroprotective drugs, niacin.
- Oral chondroprotectants - glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate. Taking them regularly can help stop damaging changes in cartilage. Chondroprotectants are built into the cartilage tissue framework, thereby increasing bone matrix formation and reducing joint destruction. The most beneficial ingredients: chondroitin sulfate + glucosamine sulfate + glucosamine hydrochloride + nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). These drugs are called combined chondroprotectants.
Neuro-orthopedic measures.An important point in treating osteochondrosis is adhering to a reasonable physical activity regimen. Not only are prolonged periods of bed rest and minimal physical activity not good for the spine, they can also lead to permanent symptoms - back pain. Therapeutic Exercise (Physical Therapy)Prescribed when the patient is in good condition (especially during periods when signs of disease are diminishing), the main goal is to strengthen muscle tights. To prevent falls, improve movement coordination and function of the vestibular apparatus (relevant for elderly patients), balance discs, platforms and paths are used in exercise therapy. manual therapySevere pain in the neck. It is prescribed according to strict instructions and with special vigilance. The main goal is to eliminate pathobiomechanical changes in the musculoskeletal system. The main reason for manual therapy is pathological tension in the paravertebral muscles. Do not forget about some contraindications to this treatment, which are associated with osteochondrosis - a large number of osteophytes (pathological growths on the surface of bone tissue), which form in the fourth stage of the development of this pathology. Physiotherapy procedures in the acute phase: - ultrasound;
- Phonophoresis;
- UV irradiation;
- electric shock;
- Electrical nerve stimulation.
Physical therapy procedures in the subacute phase: - electrophoresis;
- Magnet therapy.
massage.In all types, a superficial relaxing massage with friction elements is used. Once the pain symptoms are relieved with the help of massage, they will smoothly proceed to more intense friction. When mastering acupressure (local) massage techniques, give priority to this type. The question of surgical intervention is decided strictly on an individual basis based on the indications and the patient's condition.

Precaution
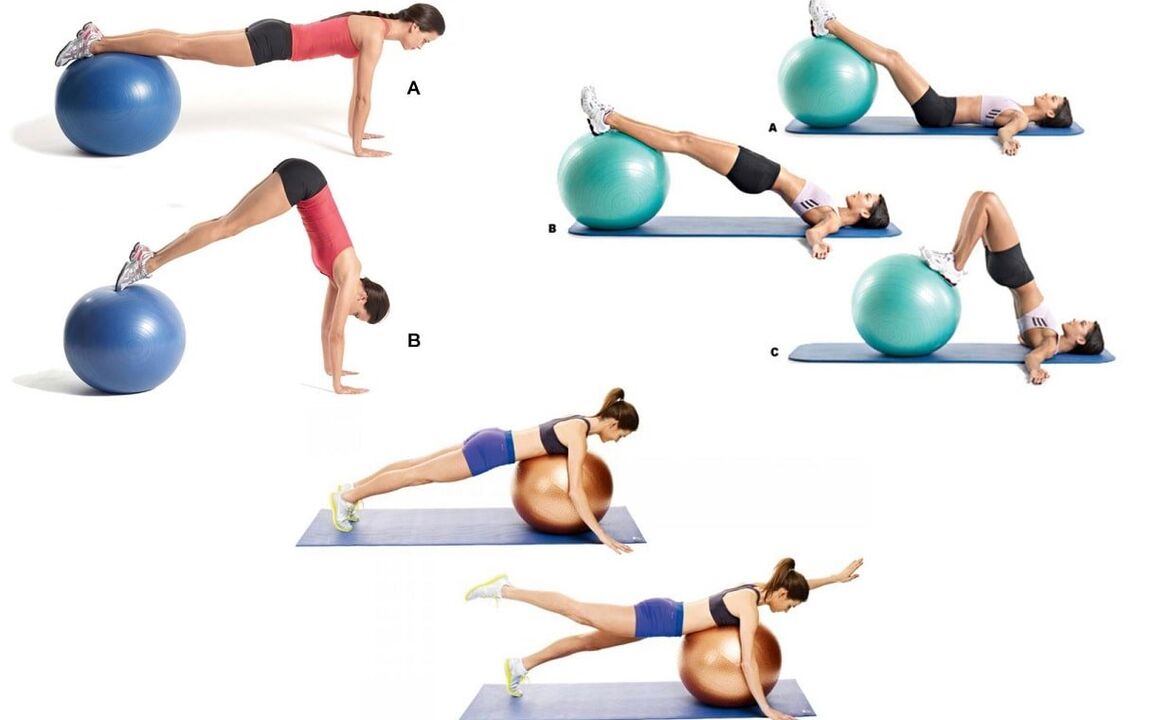

- Choose furniture correctly (especially in the workplace). Task chairs consist of a flat and sturdy backrest. The bed consists of a medium-firm mattress, a medium-soft pillow (and an orthopedic mattress and pillow if possible).
- Correction of vision, posture, bite.
- Choose your shoes wisely (especially important for drivers). Maximum heel size is 5cm.
- Wear a brace, bandage or corset while working.
- Corrective actions: Avoid bending and turning, keep your back straight and your legs bent at the knees when lifting.
- Change body position frequently: don't stand or sit for long periods of time.
- Proper nutrition: Limit intake of sweet, salty, greasy, and spicy foods. The most dangerous food for bones is white sugar because it leach calcium from bone tissue. The diet should include fruits, berries, vegetables, eggs, nuts, meat, kidneys, liver, fish, legumes and dairy products.
- Protect yourself from sudden changes in temperature; hot water from baths, saunas, swimming pools, etc. is particularly dangerous because it relaxes the back muscles, in which state even small injuries will not be felt, but willBring tragic consequences to people. the spine, and even the musculoskeletal system in general.
- The water procedure is not only a preventive measure but also a therapeutic one. Swimming combines muscle stretching and relaxation.
- Treat chronic disease.
- Active and regular vacation.
- Sit in a chair and look straight ahead. The brush covers and supports the jaw. Press your head forward and downward with resistance (tension phase); relax and stretch your neck muscles and slowly move your head back (relaxation phase);
- Sit in a chair and look straight ahead. Place your right palm on your right cheek. Slowly tilt your head to the left, try to touch your left shoulder with your ear, and maintain this position for 3-5 seconds. Place your left palm on your left cheek and do the same to your right shoulder;
- Sit in a chair and look straight ahead. Put your hands on your knees. We tilt our head to the right, hold it for 5-7 seconds and very slowly return to the starting position. Then we tilt our head to the left and do the same accordingly.